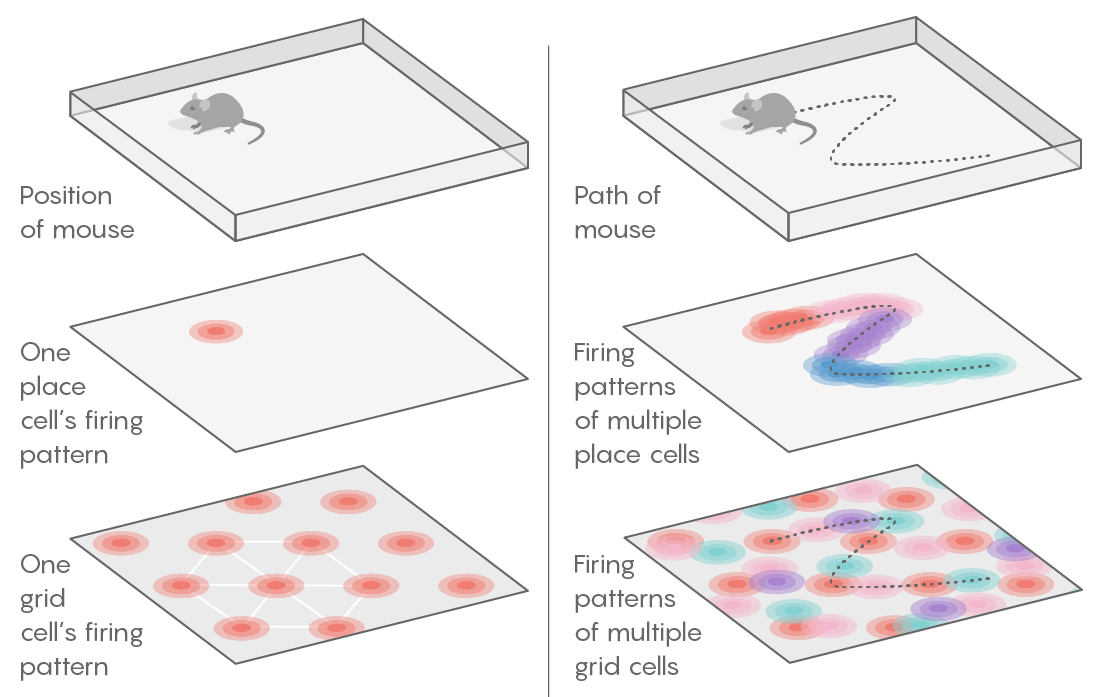
Tutorial
Get the cognitive map running
- The system runs with Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 16.04.
-
The python classes used are:
- stateMachineClass.py: the system uses a stateMachine.
- nealCoverClass.py: neal is the Neuromophic Embodied
Agents that Learn project. The idea is that we write agents
by combining modules (like the associative memory or the
parser). Then we change one parameter (the simulator), and
the system works on different platforms. Unfortunately some
PyNN functions differ from simulator to simulator. These
are included in nealCoverClass to reduce the amount of
branching (e.g.if simulator == nest) in the modules.
- cogmapClass.py: this is driven by
the stateMachineClass.py that manages the binding and
the retrievals. Initially, (startState) it waits for
a binding event. It then tryToBind, which uses a timer
since it takes time to bind. If it succeeds it goes to
bindOnState.
bindOn turns on the bindingTimer. The
bindingTimer turns on bindDone state
(bindDone starts via bindDoneTimer.)
Fail states occurs with bindFailState twoPlacesFact,
twoObjectsFact, and notEnoughPlaceObjectsFact.
retrievePlaceState is turned on externally by a
query. It turns off start. It allows the binding nets to
fire, and when a place fires, it turns on
the placeRetrievedFact (extra neurons in the
automaton net). Together these turn
on retrievePlaceDone, which then goes back
to startState A similar mechanism is used
for retrieveObject.
- timerClass.py: this makes several different types
of timers and provides mechanisms for the timers to effect
other states and be turned on by other states, spike sources
and neurons.
-
The test files are:
- runNestTests.sh: automated script for testing nest.
- testNestSimp: just test the initial state:
- testNestBindFail: build a two object three place
cogmap. There are three ways to fail. Call this with the
way you'd like. The first is to have two places. The
second is to have two objects. The third is to have one
object and no places (or vice versa).
- testNestBindOnce: using a spike source, use a bind signal,
a place and an object.
A full test of the FSA with one binding. States go from
Start to Try with the bindSignal, try to bindOn with
the onePlaceOneObjectFact
bindOn to bindDone with the end of the
bindingTimer. bindDone back to start
via bindDoneTimer
- testNestBind: test the binding of one object place
pair.
Check by turning on a place with the
object coming on because their bound.
- testNestDoubleBind: build a two object three place
cogmap.
Bind two pairs, then bind the 0
object to the second place. This is ok here, but
will cause problems with retrieve on the 0
object. However, you can notice the 1 place
comes on during binding of the second.
- testNestFull: using a spike source, use a bind
signal, a place and an object. Then retrieve one of the
bound objects by asking, and presenting its mate.
- testNestMultBind: see the following tutorial block.
Tutorial on Multiple Bind Test
- In this tutorial, the testNestMultBind will be run and
its results will be explored.
-
The test builds a five objects five place cogmap.
It tests where the objects are and what objects have places
Criteria:
object 0 is in place 1
object 1 is in place 0 and 2
object 2 is in place 1
object 3 has no place
object 4 is in place 4
---> so, place 1 has both objects 0 and 2
---> so, object 1 has both places 0 and 2
---> so, object 3 has no place as place 3 has no object
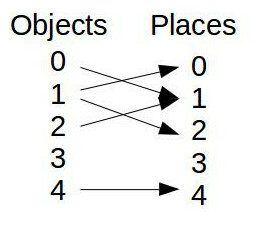
- For example, a realistic representation of the above example is the following:
- your magazine (obj 0) is on your desk (place 1)
- your laptop (obj 2) is also on your desk (place 1)
- your food (obj1) is in the fridge (place 0) that belongs to your house (place 2)
- you don't have a Ferrari (obj 3) in your garage (place 3)
- you have a bike (obj 4) in the job parking area (place 4))
- Run the test as follow:
testNestMultBind.py
- Convert the Pkl File in textual file and put it into the
autoResults directory
python printPklFile.py results/cmAutomaton.pkl > autoResults/nestMultAutomaton.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmObjectBindOn.pkl > autoResults/nestMultObjectBindOn.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmObjectBind.pkl > autoResults/nestMultObjectBind.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmObjectBindDone.pkl > autoResults/nestMultObjectBindDone.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmPlaceBindOn.pkl > autoResults/nestMultPlaceBindOn.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmPlaceBind.pkl > autoResults/nestMultPlaceBind.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmPlaceBindDone.pkl > autoResults/nestMultPlaceBindDone.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmTryToBindTimer.pkl > autoResults/nestMultTryToBindTimer.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmBindingTimer.pkl > autoResults/nestMultBindingTimer.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmBindDoneTimer.pkl > autoResults/nestMultBindDoneTimer.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmAnswerObject.pkl > autoResults/nestMultAnswerObject.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmAnswerPlace.pkl > autoResults/nestMultAnswerPlace.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmQueryOnPlace.pkl > autoResults/nestMultQueryPlace.sp
python printPklFile.py results/cmQueryOnObject.pkl > autoResults/nestMultQueryObject.sp
- Display numerically a specific result: e.g., the
nestMultQueryObject.sp
more autoResults/nestMultQueryObject.sp
- Use
Pandas and matplolib libraries to open the text file and plot it